The Science & Significance of Pink Pigments in Plants
-
Pink houseplants are like living pieces of art, bringing a vibrant burst of color to your indoor space. From soft pastels to striking magentas, these botanical beauties have captivated the hearts of plant enthusiasts worldwide. But have you ever wondered what makes them so special and how to keep their pink hues vibrant over time? In this article, we're diving into the fascinating world of pink houseplants and unraveling the secrets behind their stunning pigmentation.

What Makes a Plant Pink?
The pink coloration in plants is primarily the result of pigments. Two pigments, in particular, play a significant role in creating those captivating shades of pink: anthocyanins and betalains.
- Anthocyanins: Are water soluble pigments that are responsible for the red, purple, and blue colors in plants. In the presence of varying pH levels, anthocyanins can manifest as shades of pink. The more acidic the plant's cell sap is, the deeper the pink color will be.
- Betalains: While anthocyanins are the primary pink-pigment players, some plants, such as certain cacti and succulents, feature betalains. These pigments are responsible for red, violet, and, yes, pink colors. Betalains are not affected by pH levels so the hue won't be effected by your soil.
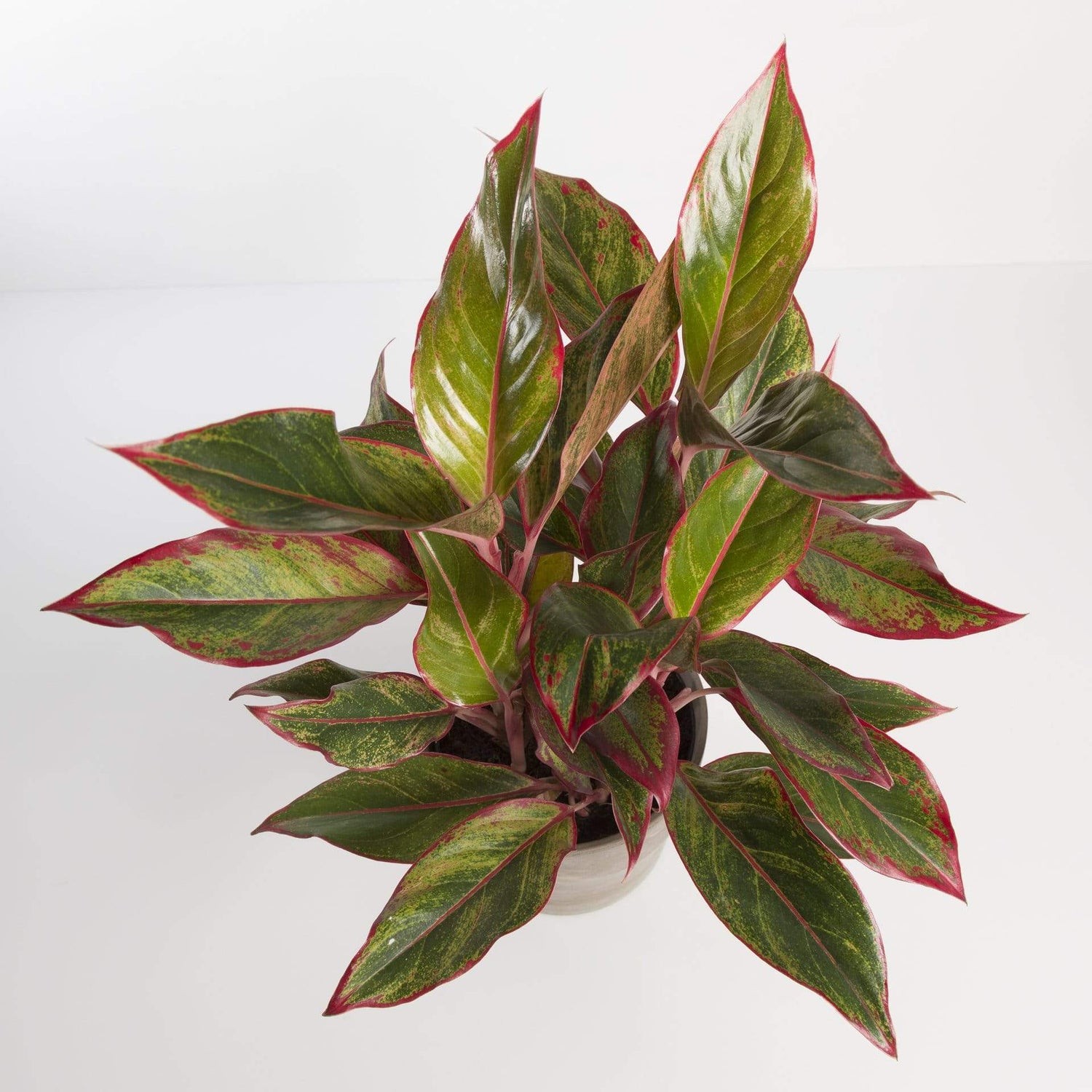

Why are some plants pink?
Plants have evolved to display pink pigments in their leaves and stems for a variety of reasons, each offering unique advantages for their survival and reproduction. Here are some of reasons a plant could evolve to have pink leaves.
Attracting Pollinators
Pink pigments, particularly anthocyanins, can act as visual signals to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. By displaying pink hues, plants increase their visibility and the likelihood of being visited by pollinators, which aids in the transfer of pollen and, consequently, reproduction.
Sun Protection
Pink pigments, like anthocyanins, can serve as a form of protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation. In high-light environments or at high altitudes, where UV exposure is intense, plants may produce pink pigments to shield their cells from damage, preventing mutations and cell death.
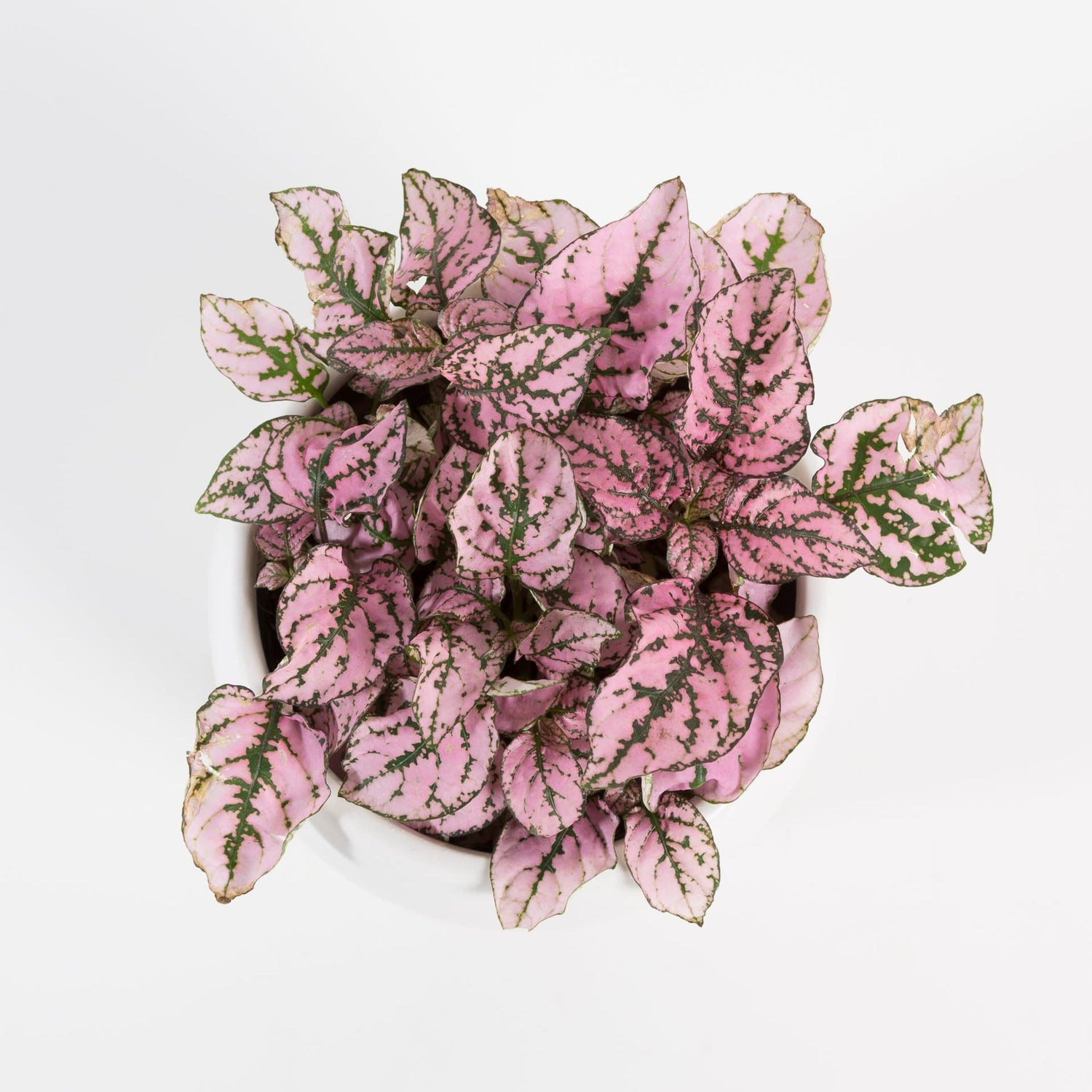

Temperature Control
Pink pigments can absorb excess light energy, helping to regulate the temperature of the plant's tissues. In hot and sunny conditions, they absorb some of the light energy, preventing overheating and potentially reducing water loss through transpiration.
Nutrient Uptake
Some pink pigments, such as betalains found in certain cacti and beets, are water-soluble and may aid in the absorption of essential nutrients from the soil. They help the plant to efficiently take up nutrients even in arid environments where water may be limited.
Defense
The coloration of pink pigments can deter herbivores. Some plants use the bright pink colors to signal that they are unpalatable or toxic, preventing animals from feeding on them.
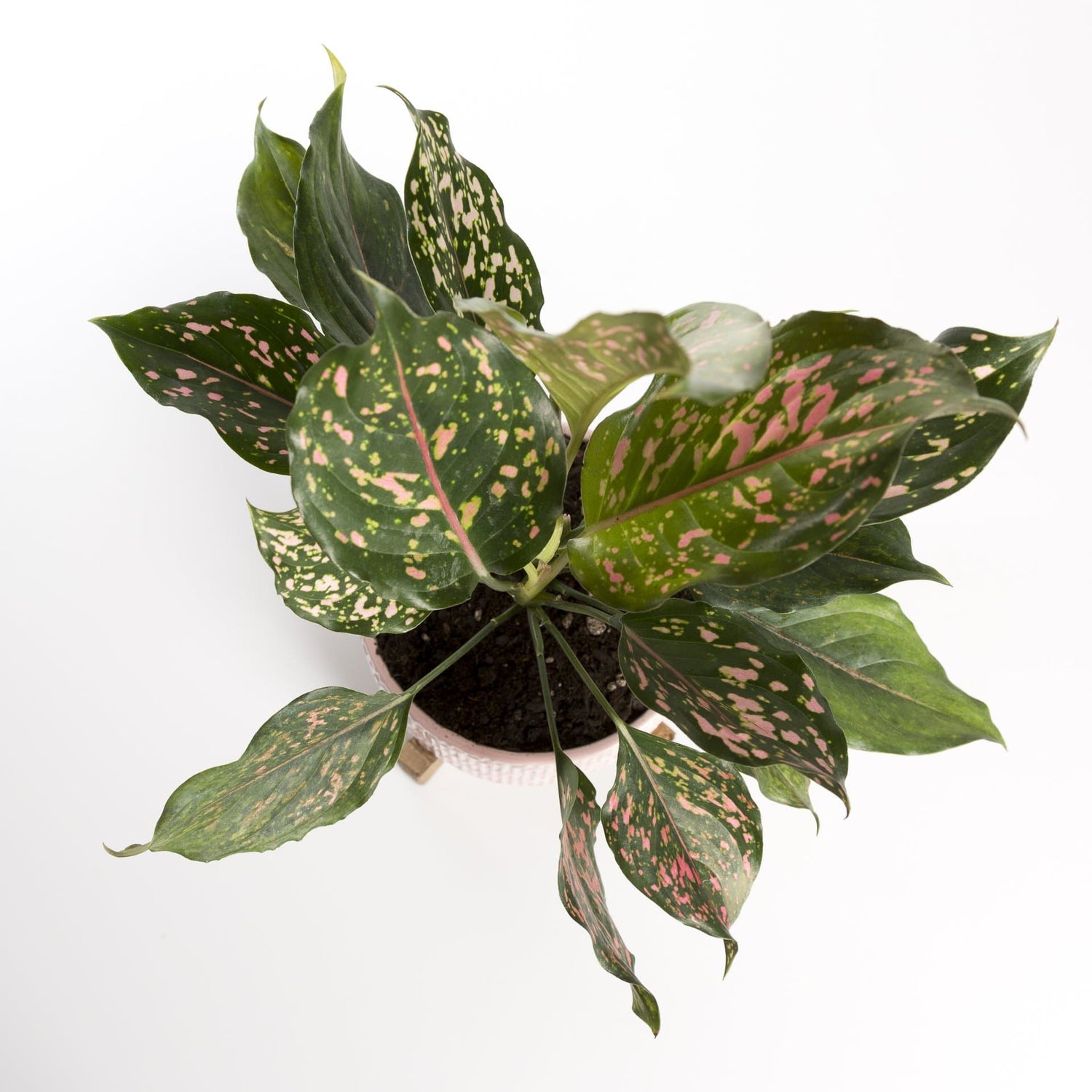

Stress Response
Pink pigments can also be produced in response to environmental stress, such as drought, extreme temperatures, or nutrient deficiencies. They may help protect the plant's cells from stress-related damage.
Camouflage
In some cases, pink pigments can act as camouflage, helping plants blend into their surroundings. This is particularly important for plants growing in rocky or desert environments where pinkish hues can mimic the colors of the terrain.
Human Interest
Many houseplants and flowers have been bred by humans over may generations to select for traits we find desirable such as larger blooms, variegation, and even those pink leaves.

Tips for Keeping Your Pink Plants Vibrant
In general the best way to really pop those pink colors of your plants is to make sure they're getting the right care. Here are a few conditions to keep in mind:
Light
Adequate light exposure is the most important factor in retaining pink pigmentation. Ensure your pink houseplants receive light exposure near the upper end of their tolerance range in order to keep those hues as vivid as possible. Lower light may lead to paler color.
Watering
Overwatering can cause root rot and adversely affect pigmentation due to spotting or paleness. Find the right watering schedule for your pink plant and be mindful of any drainage issues.
Appropriate Soil
Use well-draining soil to prevent waterlogged roots. This will help maintain a healthy plant, which is essential for vibrant colors.
Avoid Temperature Extremes
Sudden temperature fluctuations or exposure to extreme cold can cause stress to your plants, potentially affecting their pink coloration. Keep them in a stable environment to help keep that color bright.
Remember, your plant care journey is about nurturing a collection that enriches your life and brings you happiness.
If you need any help we're always just a call, click, text or visit away.
Your filters didn’t match any products
Clear All
Blogs you might like to read